
What is this disease with such a complicated name - Coxartrosis?.. This disease is a deforming arthrosis of the hip joint and is often called osteoarthrosis of the hip joint.Currently, coxarthrosis is a leader among diseases of the muscular system, which is natural degenerative-district in nature.There are many reasons for the onset of Coxarthrosis disease and in this regard, this disease has become widespread in all age groups.
Coxartrosis belongs to arthrosis that do not have an inflammatory nature, in which there are initially changes in a degenerative-district nature in the hip node cartilage, which lines the surfaces of the articular bone, and in later stages there are already direct bone changes.During such a gradually developing course of coxarthrosis, there is a violation of the normal natural functions of the affected hip joint, which, ultimately, leads to a violation of the functions of a sick person's muscular apparatus, in general.
For the most part, hip arthritis is suffered by people over the age of forty.Of course, coxarthrosis, like other diseases, seems possible to be treated successfully without surgical intervention, but only in its early stages.But in its later stages, it is unlikely to do without surgery, and only one thing can help to avoid disability - the prosthetics of the joint coexistence of the joint.Unfortunately, people sick, without joining minor pain in the hip joint in the initial stage of the disease, avoid the search for a doctor and the hip osteoarthritis, meanwhile, continues to progress the day after the day, gradually turning into a more neglected form.
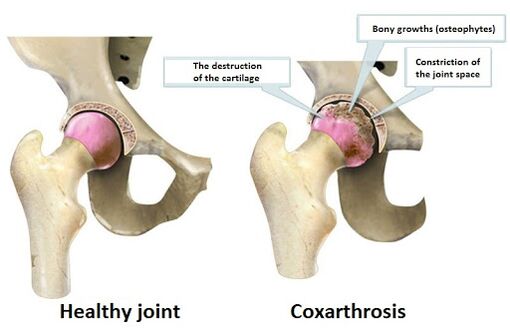
How Coxartrosis develops
Let's look at the coxarthrosis development mechanism of the disease.And we begin with the fact that the hip node consists of two bones:
- The bottom of the femur, similar to a ball;
- Return, similar to a small lush billiard placed in the iliac pelvis;
- a particular joint cartilage on the surface of both bones, which resembles a substance such as a sponge and indispensable as a shock shock absorber, which is compressed during movement and is directed in its absence;
- as well as the ligaments that form the hip fusion cavity and thus form the joint capsule.
Surrounded by the union, in addition, there are muscular, somewhat femoral, gluteal and other muscles, whose functioning also depends on the condition of the hip node.
During movement, when compressing articular cartilage, a specific fluid is "squeezed" to the joint, which is a type of lubricant for the bones that are articulated in the joint.Also, the articular cartilage itself, in addition, performs the uniform distribution of loads on the surface of the joint, being an excellent shock shocking during movements.
The emergence of coxarthrosis, is largely due to the fact that the power of the hip node cartilage is disturbed.The jump becomes thinner and then disappears in places.If you do not take measures to stop this process, then in those places where the cartilage cartoon occurs described above, the bone itself will grow directly, thus trying to "fill" the void of the common cavity with yourself.As a result of such bone changes, therefore, osteophytes begin to appear, that is, "rivets" in the bones.These deformities, in turn, lead to a bone congruence violation articulated in the hip joint and the subsequent "erosion" of still healthy articular cartilage sections.
Causes of hip joint arthrosis
The causes of the coxarthrosis with which it arises can be divided into primary, with vague and secondary etiology, as a result of other diseases, for example, such as:
- the relocation of the thigh, which is born;
- femoral dysplasia;
- Aseptic necrosis of the femur's head;
- Previously transferred various injuries, such a fracture of the neck of the thigh;
- There are diseases;
- Inflammatory processes in the hip joint;
Since Coxarthrosis disease is found not only for one, but at the same time both hip joints, it is quite possible to say that bilateral coxartrosis is a rarity.Although with primary coxarthrosis, the knee joint or spine is often affected.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
The first symptoms of coxarthrosis depend directly on the degree of damage to the hip joint, as well as the stage of development of this disease, and the main ones are:
- The pain manifested during movement, in the hip joint and disappeared at rest;
- that arise from dementia;
- stiffness that appeared in the hip node;
- declining progress of amplitude of hip movements;
- The weakness of the femur muscles and a marked decrease in their volume.
Separately, we consider the symptoms of coxarthrosis depending on the degree of the disease with this disease:
- Symptoms of 1 degree of coxarthrosis: in the hip joint there are pain that is moderate, and only after the union underwent an intense load for a long time.After removing the load and resting, this syndrome is completely stopped.In the first degree, the symptoms of walking coxarthrosis remain common and the volume of common movements does not change.
- Symptoms of the 2nd degree of coxarthrosis: pain in the hip joint is felt more intense than in the first degree, but in addition, they are designed in the inguinal region.Due to the developing muscle atrophy, the knee begins to get sick and knee, and often strongly.Sometimes, with symptoms of second -degree cokesarthritis, the pain begins to appear at rest, and after load on the affected joint, a fairly long rest is already required to stop it.Nearby starts to appear when running or walking for a long time.At the same time, the strength of the hip muscle is quite reduced, and the volume of joint movements is also underestimated.
- Symptoms of the 3rd degree of coxarthrosis: a constantly pronounced pain syndrome in the hip joint, not passing even after an extremely long or constant rest at rest, even at night.The pain is already completely affected by the whole leg.Against the backdrop of pain, the sick man develops insomnia and various sleep disorders.There is a strong atrophy of the thighs, buttocks and lower legs, while the volume of the motor of the joint is almost minimal.When walking, a sick person in order to move around is forced to be directed to auxiliary tools, such as a cane for example.
If such arthrosis of the hip joint develops only in the hip joint of one foot, then its weakened femur muscles give an impetus for the development of the pelvic lateral displacement, which reduces the length of the foot with the joints affected by the coxarthrosis.
Diagnosis of coxarthrosis
When making the diagnosis of coxarthrosis, the symptoms of coxarthrosis, described above, are taken into account, in combination with the data obtained of an X -Ray examination of the patient, consider.Such a technique provides the possibility of determining not only the degree of coxarthrosis, but to identify the causes that served as catalyst for the development of coxarthrosis.Radiography provides an excellent opportunity for determining the changes that lead specifically to damage to the hip node area, which is directly related to coxarthrosis development mechanisms.
In addition to the already listed methods of diagnosis, calculated methods of tomography and the image of magnetorsonance can also be used, providing the possibility of a detailed study of developing pathology, such as, for example, bone tissue, whose deformation is a satellite of this disease.Regarding the image of magnetic resonance, this method still allows the evaluation of pathological disorders, which underwent the soft tissue surrounding the joints affected by coxarthrosis.

Hip joint arthrosis treatment
The choice of treatment for coxartrosis depends directly on the symptoms of this disease and its stage.Typically, in the first and second degree of hip joint arthrosis, a traditional-conservative medication therapy is performed, consisting of a intake of chondroprotectors, vasodilating medicines and, according to indications, also muscle relaxants.In the period when using coxarthrosis is particularly acute, non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs are used.It should be borne in mind that such treatment should be performed by a specialist, as drug self-medication, unlike traditional medicine, can have an extremely negative effect on the patient's internal organs and fully suppress the ability to restore hyaline cartilage.
Also, with the arthrosis of the hip joint, various physiotherapeutic procedures and exercise therapy are determined.
Particularly effective, combined with the traditional treatment of hip joint arthrosis drugs, is the use of the magnetotherapy method.The method of magnetotherapy in the early stages is particularly effective - avoids dystrophic changes and returns the disease again.In later stages, the method increases the performance and quality of life, reduces the risk of complications in the affected joint.
The impact on the patient's body with coxarshrosis does not have a therapeutic effect directly with a diet, but it is recommended to obese people to reduce body weight, as it makes it possible to reduce the load on the affected joint, thus alleviating the acute symptoms of coxarthrosis.
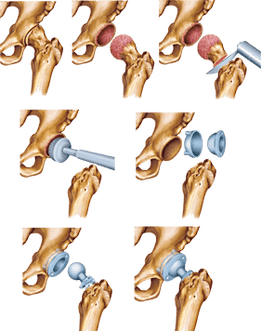
As for the third degree of coxarthrosis, the symptoms of which are more painful, treatment, as such, is performed only through surgical intervention, for example, an endoprosthetic hip node is performed.
The endoprostese includes ingredients that are functional analogs of the hip joint.This orthopedic product is installed within the limbs, which is determined by its name (endo - from the Greek "inner").An artificial replacement for hip joint performs a muscular function, but unlike the natural fusion in it, the lubricating fluid does not occur.Yes, it is not required, as this prosthesis is made of materials that, without any lubrication, slide lightly and do not destroy.
Statistical data show that after surgery, the absolute restoration of limbs with deformation arthritis of the hip joint is achieved in 95% of cases, which makes it possible to lead a very active lifestyle.
The life of such a prosthesis is about 15 ... 20 years, but at the end of its service, a second surgery is required to replace a worn endoprostese.
Please noteIt's important!Do not diagnose yourself!In the case of symptoms of coxarthrosis, you should consult an orthopedic doctor, as only a qualified specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the most optimal treatment.
Preventing Coxarthrosis
Coxarthrosis disease can also be avoided if the necessary prevention of coksartrosis is performed:
- mandatory and timely treatment of node diseases that are inflammatory;
- timely treatment of joint dysplasia;
- Compulsory physical activity accurate and reasonable, especially weight exercises to be performed correctly;
- Mandatory control of your body weight, with its maintenance normally;
- Prevention of common damage.


















